HFS Plus or HFS+ is a file
system developed by Apple Inc. to replace their Hierarchical File System
(HFS) as the primary file system used in Macintosh computers (or other
systems running macOS). It is also one of the formats used by the iPod
digital music player. HFS Plus is also referred to as Mac OS Extended
(or, erroneously, “HFS Extended”), where its predecessor, HFS, is also
referred to as Mac OS Standard (or, erroneously, as “HFS Standard”).
During development, Apple referred to this filesystem with the codename
Sequoia.
Mac OS Extended format is
Supported by Mac OS 8.1 and Later.
HFS+ always tries to write
the file on a contiguous block:
HFS+ always tries to write the file on a contiguous block In terms of
fragmentation, the file system will try to find a contiguous block of
free space, which will have enough space to fit the new file. This also
works for any file undergoing revision. The newer version will be
written as a whole, instead of in pieces. This also allows for faster
writing and file saving.
Mac’s
Hierarchical File System Plus was designed to solve fragmentation
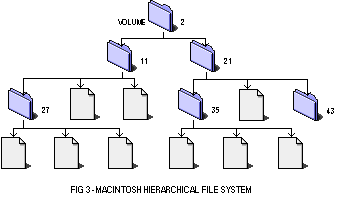
Not all computers, however, need to
defragment their hard disks. That is not to say that fragmentation
occurs, only that whatever fragmentation does happen resolves itself
internally as part of the file system. The Mac OS X uses the
Hierarchical File System Plus (HFS+), which is a based on the older HFS
system used on the Macintosh Plus and later systems, up to Mac OS 8.1.
The advantage of HFS+ is that it is a journaling file system, which
helps in data recovery in the event of a power interruption while the
hard disk is writing data to the disk. The methods used by a journaling
system also enables the file system to be able to defragment on the fly,
or while the computer is running.
What are the differences
between Mac OS Extended format and Mac OS Standard format?
The most visible difference
between Mac OS Extended format and Mac OS Standard format, other than
the minimum file size, is the maximum number of files.
HFS Plus is an
improved version of HFS, supporting much larger files (block
addresses are 32-bit length instead of 16-bit) and using
Unicode (instead of Mac OS Roman or any of several other
character sets) for naming the items (files, folders) –
names which are also character encoded in UTF-16 and
normalized to a form very nearly the same as Unicode
Normalization Form D (NFD) (which means that precomposed
characters like å are decomposed in the HFS+ filename and
therefore count as two characters and UTF-16 implies that
characters from outside the Basic Multilingual Plane –
typically seldom-used characters or those from ancient
writing systems – also count as two characters in an HFS+
filename).
HFS Plus permits filenames up to 255 UTF-16
characters in length, and n-forked files similar to NTFS,
though until recently, almost no systems software took
advantage of forks other than the data fork and resource
fork.
HFS Plus also uses a full 32-bit allocation mapping
table, rather than HFS’s 16 bits. This was a serious
limitation of HFS, meaning that no disk could support more
than 65,536 allocation blocks under HFS. When disks were
small, this was of little consequence, but as
larger-capacity drives became available, it meant that the
smallest amount of space that any file could occupy (a
single allocation block) became excessively large, wasting
significant amounts of space. For example, on a 1 GB disk,
the allocation block size under HFS is 16 KB, so even a 1
byte file would take up 16 KB of disk space. Unlike most
other file systems HFS Plus supports hard links to
directories. Like HFS, HFS Plus uses B-trees to store most
volume metadata.
The size of an allocation block is the chief distinguishing feature
between the volume format known as the Hierarchical File System (HFS)
and the newer, and optional, Hierarchical File System Plus (HFS+)
introduced with Mac OS 8.1. The differences are as follows:
-
HFS (Mac OS Standard Format). For
HFS-formatted volumes, the File Manager can access a maximum of
65,535 allocation blocks on any volume. For small volumes, such as
volumes on floppy disks, the File Manager uses an allocation block
size of only one logical block. However, the larger the volume, the
larger is the allocation block. For example, on a 500 MB volume, the
allocation block size is 8KB under HFS.
-
HFS + (Mac OS Extended Format). For
HFS+-formatted volumes, the File Manager can access a maximum of
4.29 billion allocation blocks on any volume. This means that even
huge volumes can be formatted with very small allocation blocks.
HFS+ continued as the primary Mac OS X file
system until it was itself replaced with the release of the
Apple File System (APFS)
with macOS High Sierra in 2017.


