|
|
| 
|
|
FL Studio:
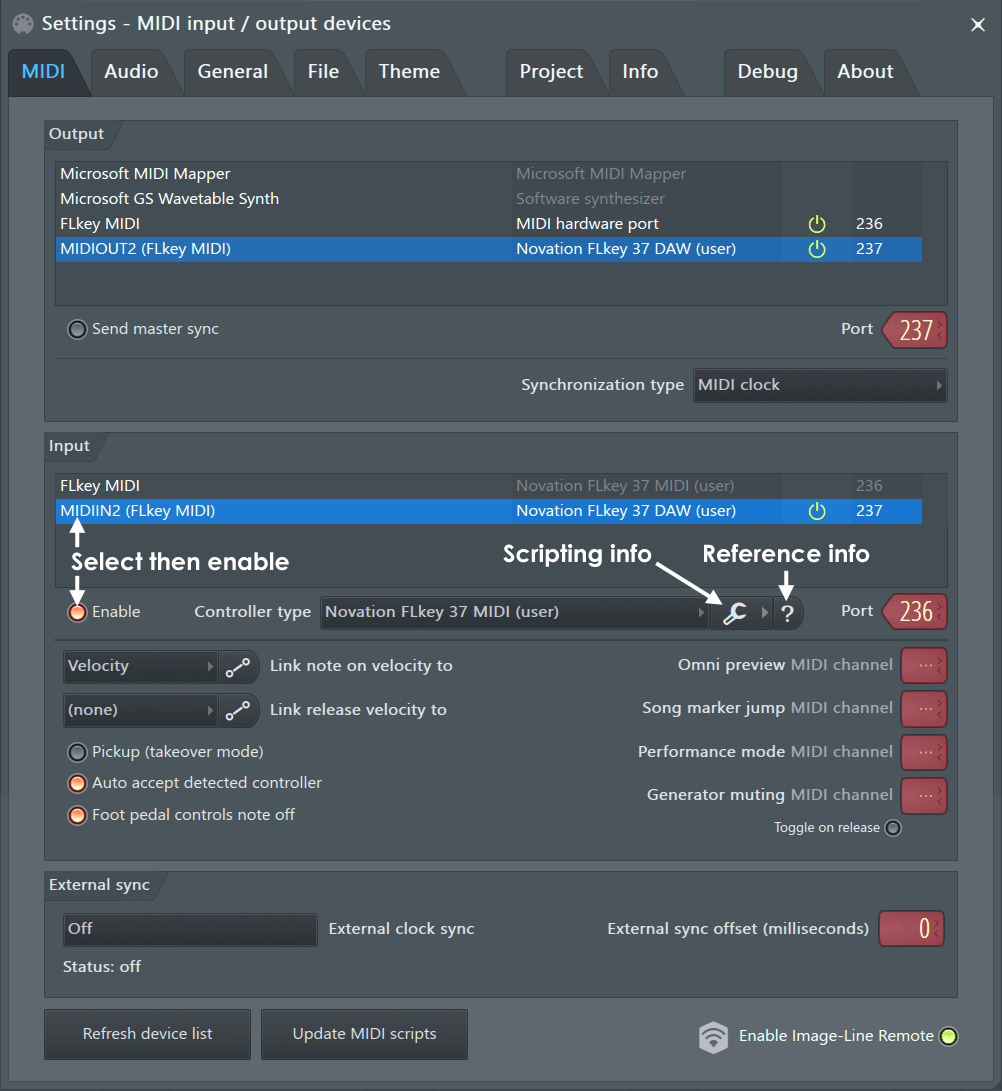
System Settings - MIDI
       
To open the MIDI Settings choose 'Options
> MIDI settings' from the main menu or press
the F10 function key on your keyboard. The MIDI Settings page contains
settings for MIDI driver input, output and syncing. It also contains options
related to MIDI keyboard recording and automation. For a list of supported
MIDI devices, see Pre-configured
MIDI Devices. NOTE: If you have never connected a
MIDI device to FL Studio before, we recommend reading the MIDI
Wizard section of the manual first.
NOTE: MIDI does not transmit audio, it is a
control-data connection (keyboard notes, knob movements, sound/program
changes).
MIDI Output
These options are used to select a MIDI Output interface, so FL Studio can
send MIDI signals to outboard gear (Synthesizer, Drum Machine, Sampler,
etc). Click on the MIDI output interface to be used, once an interface is
selected it will become highlighted. For each interface selected you can
make independent 'Send master sync' and 'Port number' settings. While only
one MIDI Output interface can be used with FL Studio at a time, you can
daisy-chain multiple MIDI devices to the Output interface, see the note
below.
-
Output - List of
detected MIDI devices in or connected to the system. Click devices in
the list to set independent 'Send master sync' and 'Port' options.
-
Send master sync - Sends FL Studio's
transport (start/stop/pause play) commands to the enabled
device/s. NOTES: Don't enable 'Send master sync' if the device does not
use transport control as it can cause unpredictable behavior, or
crashes, in the external MIDI device. There is also a 'Global' sync
option that must also be selected under the Options
menu > Enable MIDI master sync. This
enables/disables, as a group, all MIDI devices with Send master
sync selected here.
-
Port - This is a unique channel over which
MIDI data is communicated between MIDI devices (256 Ports are
available). The option assigns a Port number to your MIDI
interface (Port numbers don't apply to external MIDI hardware attached
to a MIDI interface, just the interface itself).
To map an output MIDI device -
-
Port - Make sure
the MIDI
Out plugin/s you use to control external MIDI
hardware is set to the same MIDI Port number as selected here. The Port
number chosen is not important. Selecting '---' will free the MIDI
interface for use by other MIDI software.
NOTE: Make sure global Enable MIDI output is selected in the Options
menu, 'MIDI output' will be disabled
otherwise.
Send master sync - If the device has an
internal sequencer or other functions that make use of transport
(start/stop/pause play) commands, enable this control. Otherwise leave
it off.
NOTE: Make sure Enable MIDI master sync is selected in the Options
menu, 'Send master sync' will be disabled
otherwise.
Synchronization type - Sets the
synchronization type. This is the time/code format used for syncing MIDI
devices to play/start/stop commands, etc. MIDI clock is normally used.
See the manual associated with your external MIDI device/s for details.
NOTE: MIDI allows you to daisy-chain a number of external MIDI devices.
Connect the PC to the MIDI Output interface, then connect the first external
MIDI device to the MIDI OUT and/or MIDI IN of the Output interface. Then
connect subsequent MIDI devices to the OUT or THRU ports of the device
preceding them in the chain. Make sure to set each MIDI device in the chain
to send MIDI data OUT or THRU its own MIDI ports, as this may not be on by
default (see the manual/s that came with the device/s).
MIDI Input
These options are used to connect to external MIDI input devices. FL Studio
will connect to a wide range of external MIDI controllers and MIDI hardware.
External MIDI Clock
FL Studio will
not sync to an external MIDI clock.
To control FL Studio from other MIDI software use the Rewire
Client mode
or host FL
Studio as a VST plugin inside
the host application. FL Studio will however send MIDI Clock sync so you can
control the MIDI hardware using FL Studio as the master MIDI device, see the
MIDI Output section.
Connecting External Controller/s
These options are used to select MIDI Input devices.
If you have a USB/MIDI
keyboard or controller it can be used to control
FL Studio. The Input section displays a list of controller devices that have
been detected by the Windows operating system.
-
Input - Lists
detected devices that can be used for MIDI control of FL Studio, for
example MIDI/USB piano-keyboards and external MIDI/USB
knob-controllers. To select a device click on the name in the list and
select the enable switch below. FL Studio is preconfigured to work with
a number of controllers as indicated in the Controller
type list.
-
Enable - Enables the selected controller.
Each device in the list can be independently enabled/disabled.
-
Controller type - FL Studio supports all
generic MIDI controllers. If your controller does not have a custom
driver, select USB Audio Device (generic
controller) in this menu. Don't be concerned about using a 'Generic'
driver if your device is working correctly. However, as 'custom drivers'
supply the device name and any 'special' functions the controller may
have, it's worth checking if your controller is in the list of custom
MIDI controllers. These allow support for
'unique' controls such as transport functions, jog wheels,
ribbon-strips, relative knobs, motorized faders and custom switch
controls. If your device has a custom driver but does not show in this
list by name OR nothing is showing, try re-installing the driver that
came with the device (check the manufacturers web-site for the
latest USB driver, these are usually on the technical support or
downloads section).
Port - MIDI input port. For use with
multiple controllers and Performance
Mode. NOTE: Piano roll recording is disabled
in Performance Mode.
To connect a controller
-
Make sure Enable
MIDI remote control is selected in the Options
menu, 'MIDI input' will be disabled otherwise.
-
Click on the device in the Input list so
that it is highlighted. Your controller may not necessarily appear by
its real name 'USB Audio Device (generic controller)' is common. This
appears when the 'generic USB driver' is used to interface with the
controller (see 'Controller type' above for more details).
-
Select Enable. Each device in the list can
be selected/deselected separately.
-
If you are successful the MIDI activity
light on the Main
Panel will blink each time controller data is
received. NOTE: If the 'Debug
log' is open any MIDI data received by FL
Studio is displayed and logged, useful for learning the MIDI CC numbers
of controls or troubleshooting connections.

NOTES:
-
To create permanent
links between a controller, FL Studio and plugins use the 'Multilink
controllers' switch with the 'Override generic
links' option.
-
You can lock note data from Controllers to
Channel Rack instruments, see - Controllers
and Instrument Channels.
-
Supported controllers: For the latest list
of supported devices visit the MIDI Controller
Reference forum.
-
Controller templates - There are a number
of controller templates in the FL Studio installation folder (\Program
Files\Image-Line\FL Studio\System\Hardware specific). These templates
are loaded into the editor that came with your controller and will map
it to FL Studio. You may then be required to select the controller type
in the Input settings (if FL doesn't do so automatically).
Miscellaneous MIDI options
-
Auto accept
controller - Used when linking controller knobs/sliders to FL Studio and
plugins. When selected, the MIDI
Remote Control pop-up will close as soon as
you tweak (move) the control on your external MIDI device and the link
will be made. If this option is deselected, you will need to click the
OK button on MIDI
Remote Control pop-up to accept the controller
link and then close the box.
-
Foot pedal controls note off (how MIDI
CC#64 is used) - If selected, foot-pedals sustain the length of notes
recorded in the Piano roll. That is, the note-off event is triggered by
the release of the pedal. HOWEVER, when 'Foot pedal controls note off'
is selected, MIDI Pedal CC#64 messages never reach the plugin, as it's
captured by FL Studio. If you are using a VST pluginthat needs
sustain-pedal events, for its own purposes, deselect 'Foot pedal
controls note off' for the sustain effect to work as expected, with that
plugin.
-
Omni Preview MIDI channel - When set, a
MIDI Channel from your controller will (starting at C5) play each
Channel in the Channel
Rack. Use this for percussion/loop-triggering
where each Channel
Sampler holds a unique sample or loop
-
Performance mode MIDI channel - For use
with generic controllers to trigger Clips in Playlist window (in Performance
mode). This also enables the Typing
Keyboard to trigger clips when set to Channel
1.
-
Song marker jump MIDI channel - Set the
MIDI channel to be used to accept MIDI note data to control Playlist
Time Marker jumping. See Playlist
Time Markers section for more details.
-
Generator muting MIDI channel - Lets you
set a channel on your MIDI keyboard, where each keyboard key
mutes/unmutes a channel in the Step
Sequencer.
-
Toggle on Release - Determines how
momentary buttons/switches on the MIDI controller interact with target
controls in FL Studio. When enabled, the target control will change
state when the button is pressed and revert back to the original state
when the button is released. If off, a second click is required to
revert the target back to its original state.
-
Link note on velocity to - [none] - If
this option is selected, FL Studio will ignore note-on velocities sent
by controller input devices (MIDI keyboards, etc.) and assign a fixed
velocity to all notes (a MIDI velocity of 100 or 78% is used, 127 =
100%). Velocity enables mapping note velocity from MIDI devices to
per-note velocity sensitive plugins in FL Studio. Mod X / Mod YMIDI key
note on velocity is mapped to Mod X or Mod Y and passed to any
instruments or effects using these MOD parameters.
-
Curve - Opens the Velocity Mapping
Curve editor. This curve sets the relationship between the MIDI
controller (note on) velocity and the value passed to FL Studio.
Control points can be added with right-mouse clicks and function
curves by Left-clicking on the tension handle, as with any envelope
editor in FL Studio. For the curve to take effect 'Note on' must be
linked to one of the options shown above. TIP: If you play your
controller while the Velocity Mapping Curve editor is open, the note
velocity will be visible as a vertical line. This will help you to
tune the curve shape to your playing style.
-
Link release note velocity to - [none] -
If this option is selected, FL Studio will ignore release velocities
sent by controller input devices (MIDI keyboards, etc.) and assign a
fixed release velocity (100) to all notes. Release - Some MIDI keyboards
can send the velocity of a note release, if so this enables mapping of
note release velocity from MIDI devices to per-note release velocity
aware plugins in FL Studio. For the curve to take effect 'Note on' must
be linked to 'Release'.
-
Rescan MIDI devices - If you install a
controller after FL Studio has started, or a controller that appears in
the Input list becomes unresponsive, this option will rescan and connect
to the device.
|
| |
|

